When developing new products, there are several ways to go about it. You can discuss ideas and throw around solutions to solve a particular problem, or perhaps several to find the best one. You pick what seems like the best solution and then send the idea away to be manufactured.
By the time you’ve agreed on an idea and started the process of getting it made, however, someone else already has their solution to that problem on store shelves. How did they do it? It may be that they started earlier or had faster manufacturing times, or it may be through the use of rapid prototyping.
Taking advantage of a rapid prototyping design service is a way to speed up the process of getting a product from concept to finish. By creating a rough prototype first, you can figure out what changes need to be made and improve on both form and function, all before the product is sent to be manufactured.
Designs come out better and faster through rapid prototyping. When a company adopts it, it can give them an edge over other slower competitors, helping them to get their product designs out first.
Types of Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping can be divided up into two major design types—high-fidelity designs and low-fidelity designs. The latter designs are usually produced first because they are the fastest and simplest. A low-fidelity design can be anything from a sketch to a product mock-up made out of duct tape and cardboard. It doesn’t involve expensive materials or even have to look like the finished product at all.
The idea of this type of prototype is simply to convey the idea and look for obvious problems or changes that need to be made. Once as much data has been gleaned from a low-fidelity design as possible, the product then moves to a high-fidelity design using a prototype design engineering service.
High-fidelity prototypes are designed to look and act as close to the finished product as possible. These products may be made from cheaper materials, but are good enough to thoroughly test the product and check for errors.
These final prototypes are also used to show clients and others involved a sneak preview of the product and may also be useful in raising money.
Advantages of Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is a mainstay for many freelance product designers, and for good reason. It’s a very effective method of creating a high-quality product in as little time as possible. We all know that if you rush a product through a design process thoughtlessly, the result is often mediocre.
Creating a product from start to finish can cost hundreds and thousands of dollars, or even millions, depending on what the product is. With such a huge investment at risk, making thoughtless mistakes could result in unexpected delays as the product must be sent back for changes, or ends up not selling well.
Rapid prototyping is a method of retaining a fast process without losing the benefits of careful planning. Here are just a few of the advantages of adopting this process.
Faster Completion Times
The major benefit of rapid prototyping is that it can help speed up the process of product creation. In today’s rapidly developing market, getting your product out first can mean gaining a major share of the market before anyone else does.
RELATED: Going from Prototype Design to Finished Product
The best method of getting a product out with as few mistakes as possible is through rapid prototyping. By making a quick prototype of your product, you can test it for several different factors, making sure you’ve thoroughly worked out any bugs before sending the product to be manufactured.
This saves time by avoiding devastating mistakes but also helps with the design process. It’s much more efficient to evaluate a product that is as close to functional as possible. You may have to go through fewer rounds of testing to reach a satisfactory result.
That means an overall faster finishing time while still receiving a high-quality product.
Lower Costs
Although there may be more initial costs for getting a prototype 3D printed or sent to a manufacturer for a small run, overall production costs are generally lower. By taking the time to test a prototype before sending it to production, you reduce the risk of creating $10,000 of a product before discovering a fatal flaw.

Although using a 3D printing design service is more expensive per unit than a small run at a manufacturer, it’s often cheaper overall due to needing fewer units and it takes less time to get the product back. That can mean an overall cost saving by choosing to do the process yourself, rather than convincing a manufacturer to run a small number for you.
Testing the product with potential users can also help determine whether a potential prototype has promise and help solve issues before poor reviews come rolling in.
Elimination or Reduction of Risk
There is always an element of risk when creating a new product, but by creating prototypes before going straight to manufacturing, you eliminate many of them. Basic testing and the ability to see if a design is ergonomic or easy to use before manufacturing can make a big difference in whether people will want the product or not.
Even a relatively low-cost product can run tens of thousands of dollars to produce. Reducing the risk of this investment failing is a sensible step and worth a small initial investment.
Allows Testing
Even if a product looks good and solves a problem, it will frustrate users if it isn’t very functional. The primary purpose of a prototype is to test it to make sure not only that it is ergonomic and safe, but also easy to use too. During the testing process, you may discover a simpler design or a better way to do things.
Even if you use a 3D product modeling service for much of your testing, you should always have a prototype made to double-check the product is everything that it should be before confirming a large order. An untested product could have safety issues, or may simply be more expensive than it has to be with too many moving parts. Simple testing can be an easy way to avoid this.
Improved Buyer Involvement
Letting your users have a chance to directly interact with a prototype can help generate a buzz all on its own, as they have a chance to see and experience the product for themselves. Many companies take prototypes to trade shows and tech events to gauge user interest and gain insight into how to improve the product. A working prototype can be one more powerful tool in the quest to create the perfect product.
May Help Raise Money
For small companies or products that require a lot of capital, raising the money may be the only way to get these products off the ground. Companies such as Kickstarter and other crowdfunding sources have popped up to help fill the void for those who can’t get traditional funding, but it still leaves convincing the public to back a product.
One of the best ways to show this is through a working prototype. A functioning prototype allows investors to see the potential product and evaluate for themselves whether or not it is worth putting their money into.
In the case of crowdsourcing, an eye-popping prototype made by a prototyping design freelancer can mean the difference between exceeding fundraising requirements and never making your financial goal.
Prototypes can help a product in a variety of different ways and there’s a big benefit to using them.
Disadvantage to Rapid Prototyping
Just as with everything else in the world, rapid prototyping does have its downsides. Although rapid prototyping will save money over time, it does require an initial investment. A single item is often more expensive to build as a unit compared to a unit from a run of several thousand.
The other potential problem is that while a prototype may generate excitement from consumers who get a chance to interact with it, it may also confuse them. Prototypes may not have all their features in place yet and often don’t look exactly like the finished product will. If a customer or stakeholder sees a prototype in a fundraiser or at a tech show, they may confuse it with the final design.
These downsides can be problematic, but they don’t necessarily have to stop you from taking advantage of the many benefits of rapid prototyping. As long as you are aware of the potential problems, you can take steps to try and address them.
Methods for Producing Prototypes
Rapid prototyping is sometimes confused with 3D printing itself and these terms are sometimes even used interchangeably. 3D printing is the most common way for a freelance industrial designer to create a prototype due to the easy and cost-effectiveness of getting a single or just a few prototypes.
Rapid prototyping is the process of getting those prototypes made, not the manufacturing process used. How the prototype is manufactured is irrelevant in this case.
Prototypes can be made in a variety of different methods. Different methods may be more appropriate for different types of manufacturing. Here are just a few of the methods commonly used for rapid prototyping.
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography 3D printing services place polymers down layer by layer to form the desired prototype. In this case, UV light is used to solidify resin until the desired end product is reached. Stereolithography was invented in the 1980s and is widely used for prototypes.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective laser sintering services use a high-powered laser to melt powdered material such as glass, metal, or plastics, following a CAD model.
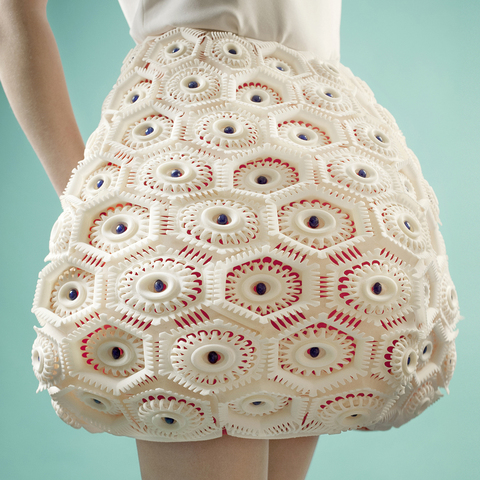

This method is very popular for rapid prototyping because it is perfect for making just a few items with high-quality materials.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Another 3D printing method, this method is most commonly used for small household 3D printers. The 3D printer uses a long plastic filament to build the product according to a 3D model.
These 3D printers work well for creating small parts and models and are popular because the results from them are very quick. There are plenty of fused deposition modeling designers out there.
Binder Jetting
In this method, powders of various sorts ranging from metals to ceramics are bound together layer by layer using a liquid binder. This method allows the prototype to be printed in color, which not all types can do so.
Poly Jetting
Poly jetting also uses liquids to create a prototype, but in this case, small drops of UV sensitive polymers are sprayed layer by layer. This type is almost consistently used for prototypes because the end product is sensitive to light and may change over time when exposed to it.
Despite this, it is very popular for prototyping due to the amazing resolution and smooth quality it can give the prototypes.
There are many other methods of producing prototypes, including subtractive types that whittle away from a block of material and additional types of additive production methods. When putting together a design for a prototype, paying attention to what method of manufacturing you will use will affect the overall finish of the prototype.
Sometimes choices are limited, such as if you want a non-plastic material or want a specific look. If appearance or quality is unimportant, however, choosing the most cost-effective method of production is best.
Cad Crowd’s Rapid Prototyping Experts Are at Your Disposal
Rapid prototyping is a great tool that can help you get your product out there as efficiently as possible, and more importantly, with a minimum of errors. It can help you stay competitive in a tough marketplace by giving you the tools you need to evaluate a product before going through the expense of manufacturing.
By using this technique to create and test your products, you’ll be ahead of the market so that the next time you are racing a competitor to release the next great idea, yours will hit the marketplace first.
Cad Crowd has a network of experienced freelance professionals waiting to assist with your project, whatever that may be. Find out how it works and get a free quote today.
