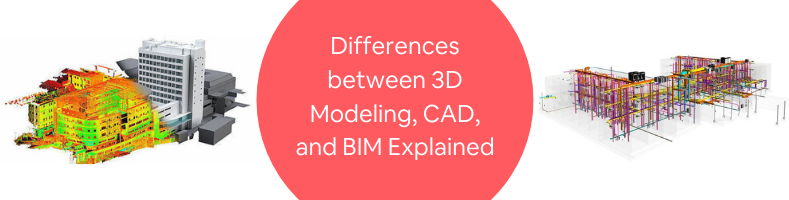
Architects and freelance engineering design services have been using computers to design and manage their projects. There is plenty of sophisticated computer software to help them create extremely detailed 2D or 3D models of just about every object imaginable, allowing them to identify and prevent mistakes long before a design is materialized or used by end consumers.
It is true that computers are now considered indispensable, but they are truly revolutionary in the design world. Designing an object on a computer almost completely eliminates the need to go through the trial-and-error phase of the work. 3D visualization services on computers make it possible to evaluate the aesthetic and performance aspects of an object while it is still in digital form.
The landscape of digital visualization is so vast that there are many confusing (perhaps conflicting) terms used; among them are 3D modeling, CAD, and BIM.
3D Modeling
It is good to start with 3D modeling design services because they service most of the industry. 3D modeling covers a broad range of disciplines so it has become the umbrella term for any type of model made on a computer. At its core, 3D modeling is the process of developing a digital representation of any object in three dimensions using a computer with specialized software.

All 3D models created on a computer—regardless of the software used—are the result of the 3D modeling process. Further divisions are made when you go into the specifics of the process, including techniques and what the objects are; case in point, CAD and BIM.
CAD
The term CAD or computer-aided design is used to describe the use of a computer to assist the design process in all sorts of industries, as well as the type of software required for the job. It comes in two different types based on the application:
- 2D CAD design services, or the use of CAD software to create two-dimensional drawings like a floor plan or technical drawing of a mechanical component. Although the technology is a little bit old-fashioned, 2D drawings created using CAD are still commonly used as official documents in many engineering environments. If need be, two-dimensional images are generated from 3D models for record-keeping purposes.
- 3D CAD models created using 3D CAD software must be accurate geometrical representations of physical objects found in real life. In some industries, including games and film, 3D CAD software is utilized to create imaginary objects such as animals, vehicles, vegetation, monsters, etc.
A large user base of 3D CAD applications includes graphic design, product design services, and engineering industries. The 3D models are more than a visualization of objects—they also serve as tools to confirm functions and evaluate performance. While it is true that some CAD software offers architectural-related features, they still lack detailed functional data typically available from BIM software.
BIM
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a highly specialized field of 3D modeling. In fact, freelance BIM modeling services are popularly used only among architectural professionals because it is specifically created to help run and manage construction projects. It involves 3D visualization of the facility or building to be constructed, but the real advantage of BIM is the amount and depth of data attached to every single component of the structure.
In addition to aesthetics or surface-level visuals, a BIM file also contains data for sub-surface construction. For example, HVAC systems, plumbing pipes, electrical wiring, and even how many bricks a wall needs.
RELATED: CAD Conversion: Do Your Drawing Conversions In-House or Outsource?
The digital representation of a structure in a BIM file must also contain functional data, which means every element knows its intended purpose and behavior. For example, a p-trap knows that it must connect to a drain pipe rather than an HVAC duct.
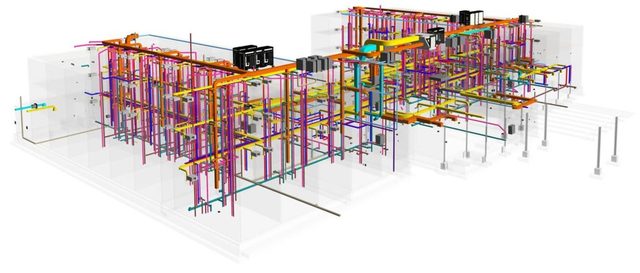
Traditional building designs are presented as two-dimensional technical drawings that contain data about elevation, section, floor plan, etc. BIM offers a massive advancement to the conventional approach by using 3D models, which are not only geometrically-accurate but also attached with detailed information regarding time/scheduling (4D), cost (5D), environmental and sustainability analysis (6D), and facility management information from the design stage to demolition (7D).
Used widely by architectural BIM services, engineering, and construction (AEC) firms, BIM software has refreshed the outdated approach to construction design with much better visualization and more accuracy.
Important Differences
The terms 3D modeling, CAD, and BIM are often confused with one another, which is quite understandable. Some professionals use the same software for all three applications, and some companies market their software with everything but specific descriptions, leading to confusion among users. There is a certain degree of overlap between the terms and their usage, but they also have some notable distinguishing properties.
RELATED: 3D Rendering Freelancers & Visualization Services vs. In-House 3D Artists
When intended to create 3D objects, CAD and BIM applications fall under the 3D modeling category. This means that all works created through the process of either CAD or BIM can be considered 3D models and the creators can be regarded as 3D artists in general.
The term CAD itself is quite broad and must be narrowed down to either 2D CAD or 3D CAD design. The term 3D CAD can be used—in nearly all cases—interchangeably with 3D modeling, but the same thing cannot be said to BIM.
You can almost say that BIM is one of the disciplines in CAD that deals primarily with building plans. However, you must remember that BIM is more than just a 3D representation of a building because the application extends beyond just a graphical representation.
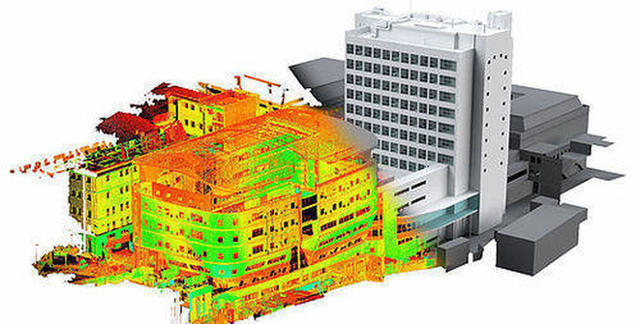
A full-fledged BIM file contains not only a three-dimensional overview of the geometry of a building, but also technical data including but not limited to spatial relationships, geographic information, quantities of building components, light analysis, and component properties or manufacturers’ details. Each element of the building may carry its attributes to provide crucial information such as cost estimates, materials, and order.
Other notable differences are as follows:
Scope of Application
3D CAD is mainly about developing hyper-realistic digital 3D models of just about any object. This is the main reason that the technology is utilized in a wide range of industries such as science, industrial design services, product design, marketing, advertisement, games, and films.
The 3D models can serve multiple purposes. For example, they can assess the technical and financial viability of a design, construction stability, function, performance, user experience, and aesthetic aspects before the object is materialized. In the game and film industries, the objects never have to be materialized because the final products will still be in digital format.
On the other hand, BIM is almost exclusively used for construction projects, so its application is limited to the architectural industry. Thanks to the monumental amount of data that BIM software can create and manage within a single file, it has become the primary choice in modern architectural and civil engineering projects.
BIM software allows professionals to evaluate every aspect and process involved in the work.
Primary Characteristics
3D CAD models contain a collection of points in three-dimensional space. Each point is connected by geometric elements such as lines, triangles, and various shapes of surfaces. Arranged properly, all those entities become the building blocks of a 3D model. Up to this point in the process, the main information stored in the model is geometric data.
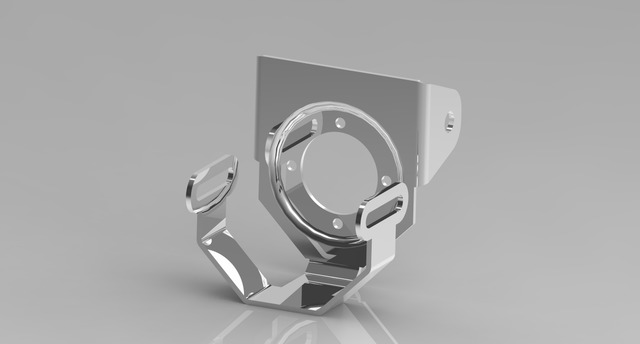
A professional 3D product modeling service can enhance the 3D model by incorporating shade and textures to the surface, making the object look more realistic. Instead of a collection of lines and points, the model now appears as if it is a solid physical object displayed on a three-dimensional space on a screen. The rendering process adds lifelike scenery digitally-built around the object to further escalate the appearance into its hyper-realistic level.
BIM can also create realistic models of a building, but it is not the main purpose or application. The biggest selling point of BIM is the way it conveys information about a building or facility. Although aesthetics remain of great importance, BIM does not regard that particular aspect as the end goal.
In fact, BIM implements such an approach to most (if not all) elements including structural systems, walls, electrical systems, HVAC equipment, plumbing fixtures, floor, doors, windows, and roofs. HVAC design and drafting services routinely use BIM.
For example, a BIM object of a wall is attached with information or annotation of its density, strength, permeability, electrical resistivity, reflectivity, and even materials, as well as the time required to build it using the available tools. Even with all the data, the wall doesn’t have to appear realistic on-screen; it only needs to be recognizable as the wall of a structure.
File Behavior
Unlike 3D models created using 3D CAD software, a BIM file made by an architectural design service behaves in accordance with its unique parameter depending on connection requirements and purpose. The model has information and functional data that allows it to behave in a specific manner.
The 3D model—despite its stand-alone attribute—knows what it is supposed to do in the environment it is placed. For example, a faucet knows that it needs to connect to a plumbing pipe, a light fixture knows it requires electrical wiring to work, and an HVAC duct knows it has to be installed inside a wall. CAD models lack this kind of functionality.
Software
Different applications require different software, but this is not necessarily true in the case of 3D modeling, CAD, and BIM. Some of the most sophisticated software in the 3D visualization industry can be used for all three applications.
| Application | Software |
|---|---|
| 3D Modeling | SketchUp, 3ds Max, Cinema 4D, Rhino 3D, CATIA, AutoCAD, Blender, ZBrush |
| CAD | SketchUp, 3ds Max, Cinema 4D, Rhino3D, CATIA, AutoCAD, OnShape, Alias |
| BIM | REVIT and ArchiCAD, Tekla, CATIA, Vectorworks, BricsCAD BIM, Microstation, SketchUp (requires PlusSpec plugin) |
Cad Crowd’s Freelancers are Experts at BIM, CAD, and 3D Modeling
At Cad Crowd, we have the privilege of working with some of the best freelance 3D modelers and CAD designers in the world. Our network of professionals has worked on projects for prestigious clients including Tiffany & Co. and Tupperware. For more information, find out how it works.